EPR REGISTRATION:
Plastic products have become an essential part of our daily lives. It is produced on a massive scale all over the world. Plastic waste is generated at approximately 5.6 million tonnes per annum (TPA) in India. Its disposal is a significant issue. Recycling is a good way to reuse plastic products but finding a way to eliminate plastic is important.
To ensure the processing of plastic packaging waste, the Extended Producers Responsibility (EPR) regime is being implemented in the Plastic Waste Management Rules, 2016. According to which, Producers, importers, and brand owners are responsible for ensuring that their plastic packaging waste is processed through recycling, re-use, or end-of-life disposal.
PIBO refers to producer, importer and brandowners. If you identify as a PIBO and have operations in India that include the use of plastic packaging, you fall under the obligation of EPR regardless of your turnover or scale of operations.
What is Extended Producer Responsibility:
Extended Producers Responsibility means the responsibilities of Producers for the environmentally sound management of the product until the end of its life.
Extended Producer Responsibility for Plastic Packaging is the responsibility of Producers, Importers & Brand Owners for the management of their plastic packaging waste.
The Ministry of Environment, Forests, and Climate Change, Government of India, notified an amendment to the PWM Rules on February 16, 2022, according to which producers, importers, brand owners (PIBOs), and Plastic Waste Processors shall comply with Extended Producer Responsibility as per Guidelines given in Schedule II of PWM Rules.
According to EPR guidelines for plastic packaging, Producers, Importers, Brand-Owners, and Plastic Waste processors shall have to register through the centralized online EPR portal developed by the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB). PIBOs shall have to obtain EPR Registration from CPCB.
PIBOs that operate in one or two states/UTs are required to register with the concerned State Pollution Control Boards (SPCB/PCC). PIBOs that operate in more than two states/UTs are required to register with CPCB.
PIBOs are required to ensure that plastic waste is processed through Plastic Waste Processors (PWPs) in accordance with an action plan in order to meet assigned EPR targets. They shall obtain a PWP certificate based on the amount of plastic waste processed by PWPs and use these certificates to meet their EPR targets.
The following entities shall register for EPR registration certificate on the centralized EPR portal developed by CPCB:
- Producer
- Importer
- Brand owner
Plastic Waste Processor engaged in (a) recycling, (b) waste to energy, (c) waste to oil, and (d) industrial composting

EPR Registration for Producer and Importer
The E.P.R. Authorization is a responsibility vested with producers/importers to properly dispose or recycle post-consumer E-waste as per the Plastic Waste Management Rules, 2016. E.P.R. stands for “Extended Producer Responsibility” is an environmental & economic approach to administering the product’s lifecycle.
It encompasses the prevention, proper disposal & systematic recycling. Primarily there are three categories of authorization, viz
- Import authorization
- Manufacturing authorization
- Wholesale authorization
It is important to note that the manufacturing authorization is most cumbersome to secure as it seeks ample infrastructure and training investment. The E.P.R. certification is a legal compulsion for Indian or overseas manufacturers or importers of electronic items for E-waste management.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
Why Government introduced E.P.R. Authorization?
With the soaring increase in e-waste, G.O.I. has examined the prevailing policy options & concluded that entrusting manufacturers and importers with responsibility could be the best way to combat such a situation.
In general, Extended Producer Responsibility refers to a policy-based approach under which manufacturers are vested with responsibility for seamless treatment or disposal of post-consumer products.
In a nutshell, E.P.R. seeks to ensure;
- Better prevention of waste at the source
- Production of environmental-friendly products
- Seamless recycling & management of e-waste
Two categories of electrical and electronic equipment namely:
- IT & Telecommunication-based item &
- Consumer electronics such as Televisions, Refrigerators, A.C., Washing Machines, mercury-containing lamps, etc
An Overview of E-Waste (Management & Handling) Rules, 2011
- E-Waste (Management & Handling) Rules, 2011, were promulgated by the government in 2011 & had come into play since 1st May 2012. To ensure seamless implementation of E-based waste rules & clearly describe the duties of producers in E.P.R., MoEF & CC, G.O.I. in the purview of E-Waste (Management and Handling) Rules, 2011, has unveiled the E-Waste (Management) Rules, 2016 vide G.S.R. 338(E) dated 23.03.2016 which came into effect on 01-10-2016
- These rules encompass every manufacturer, consumer, accumulation facility, dismantler, & Recycler engaged with the manufacturing, trading, and processing of electronic goods cited in schedule – I of these Rules.
- All these rules revolve around Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR). Target-based approach for EPR’s implementation has been inculcated in the E-Waste (Management) Rules, 2016, which render phase-wise collection target to the manufacturer for the accumulation of e-based wastes, either in weight or number, which shall be thirty per cent of the estimated quantity of waste produced during first two years of rules’ implementation followed by 40% during 3rd and 4th years, fifty per cent during 5th & 6th years & 70th during 7th year onwards.
- The E-Waste (Management) Rules, 2016 mandate the Central Pollution Control Board i.e. CPCB which entails specific norms related to EPR, channelization, accumulation facilities, storage, transportation, eco-friendly recycling, refurbishment, & sampling of EEE for testing of RoHS guidelines.
Potential benefits offered by EPR registration
The EPR registration holders access the following benefits;
- Improved goodwill in the market owing to the commitment to reducing e-waste
- Access to a definitive framework that ensures effective management of e-waste with low cost
- Ensure better coordination with allied units for e-waste handling
- Provide a credible image for international market
BANNED SINGLE-USE PLASTIC ITEMS IN INDIA
According to the Plastic Waste Management (Amendment) Rules, 2021, it will be illegal to manufacture, import, stock, sell, distribute or use identified single-use plastic products from July 1, 2022.
The list of Single-Use Plastic (SUP) items that will be prohibited from 1st July 2022 are as follows:
- Earbuds with plastic sticks
- Plastic sticks for balloons
- Plastic flags
- Candy sticks
- Ice cream sticks
- Polystyrene (Thermocol) for Decoration
- Plates
- Cups
- Glasses
- Forks
- Spoons
- Knives
- Straws
- Trays
- Wrapping/packing films around sweet boxes
- Invitation cards
- Cigarette packets
- Plastic/PVC banners less than 100 microns
Categories of Plastic packaging covered under EPR:
Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) applies to the following plastic packaging categories:
Category I: Rigid plastic packaging
Category II: Single-layer or multilayer flexible plastic packaging (more than one layer with different types of plastic), plastic sheets or similar and covers made of plastic sheets, carry bags, plastic sachets or pouches
Category III: Multi-layered plastic packaging (at least one layer of plastic and at least one layer of material other than plastic)
Category IV: Plastic sheet or like used for packaging as well as compostable plastic carry bags
Documents required for EPR registration of PIBOs/PWPs
- PAN, GST, CIN,
- IEC (for importer) of the Company
- Aadhar / PAN of Authorized person
- DIC Registration (if the unit is registered with DIC)
- Process flow diagrams (for producers & PWPs only)
- Consents issued by SPCB/PCC (if the unit has a production facility)
- Scanned copy of signatures of authorized persons.
- Covering letter
Geo-tagged pictures of raw material storage area, production area, product dispatch area, and plant machinery (in case of PWPs only)
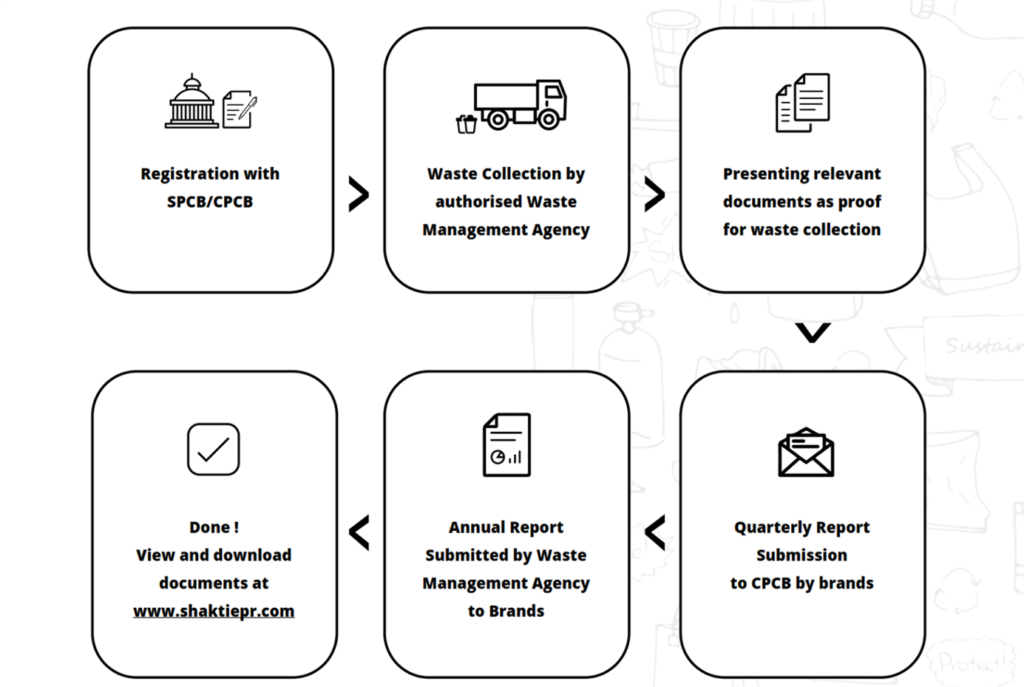
PROCESS OF EPR REGISTRATION
To obtain EPR registration certificate, PIBOs shall submit an online application along with the necessary information, documents, and application fees.
Validity, Renewal & Cancellation of EPR Registration
A new registration shall be valid for one year, and a renewed registration shall be valid for three years.
PIBO shall submit the renewal application, along with the required documents, four months before the expiry of the Registration.
EPR registration granted to PIBOs may be cancelled or suspended at any time if the document submitted by the PIBO is found to be false.