The BIS’s new guidelines help India achieve its sustainability and environmental goals. As India works to decrease its carbon footprint and promote green transportation, these standards will help ensure a seamless and safe transition to electric mobility.
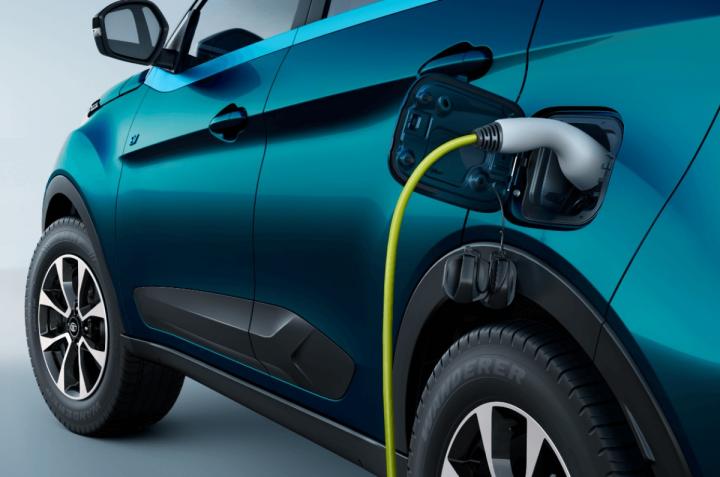
The Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) has issued two new standards, IS 18590: 2024 and IS 18606: 2024, to improve the safety and quality of electric vehicles in India. These criteria, which apply to vehicles in the L, M, and N categories, focus on the crucial component of electric vehicles—the powertrain—to ensure it pass severe safety requirements. They also prioritize the safety and performance of batteries, ensuring that they are both powerful and safe.
Recognizing the growing popularity of e-rickshaws and e-karts, BIS has also issued IS 18294: 2023, which specifies safety norms for these vehicles. This new standard addresses a variety of issues, from construction to functionality, ensuring the safety of both drivers and passengers.
With these improvements, BIS now offers 30 Indian Standards specifically for electric vehicles and their accessories, including charging systems. These broad criteria are critical in propelling the country’s transportation sector toward a more sustainable, environmentally friendly, and efficient future.
Impact On the EV Industry
The development of these standards by the BIS is a key step toward improving the safety and quality of electric vehicles in India. These guidelines protect the reliability and security of EVs on Indian roads by establishing high safety requirements for powertrains and batteries. This program is expected to increase consumer trust in electric vehicles, boosting their adoption across the country.
Furthermore, the inclusion of standards for e-rickshaws and e-karts demonstrates BIS’ commitment to an all-encompassing approach to electric mobility. These guidelines ensure that the advantages of electric vehicles extend beyond cars and trucks to other modes of transportation, making electric mobility more accessible and safe for a wider range of people.
Understanding Vehicle Classifications
Vehicles are categorized into the L, M, and N categories according to their intended function and technical features. Regulations and standards frequently make use of these classes to guarantee that the proper safety and performance requirements are satisfied for various vehicle types.
2Ws and 3Ws are included in the L category. These are further separated into L1 (2Ws, which have a maximum continuous rated power of no more than 4 kW for electric motors a maximum design speed of no more than 45 kmph, and an engine size of no more than 50 cc for internal combustion engines.
L2 is for 3Ws with comparable power and speed limitations to L1. L4 is for motorcycles with sidecars, and L3 is for 2Ws without a speed limit, usually motorbikes.
Vehicles built and intended for passenger transportation fall under the M category. This category is further divided into M1, which is for cars that are normally built with a maximum of eight seats in addition to the driver’s seat and are intended for passenger transportation.
Vehicles designed to transport more than eight passengers in addition to the driver fall into the M2 category; vehicles meant to carry more than eight passengers in addition to the driver fall into the M3 category; vehicles designed to carry more than eight passengers in addition to the driver fall into the M3 category.
Vehicles built and intended for the carriage of goods fall under the N category.